Select the best font pairs that look good together for your project.
Create a business name and logo for your business brand
We've generated some logos for you
Convert your images to favicon files
Upload your favicon and we will make favicon asset package. Copy the text in instructions to the top of your html site.
Place the converted files in the root directory of your website. Then, copy the following link tags and paste them into the head of your HTML.
Chose your brand base color:
Primary Color
Accent Color 1
Accent Color 2
Complement Color
Accessible Color
Compare colors between two images and get detailed analysis
Choose matching colors that will fit your brand.
Select points:
RGB(A):
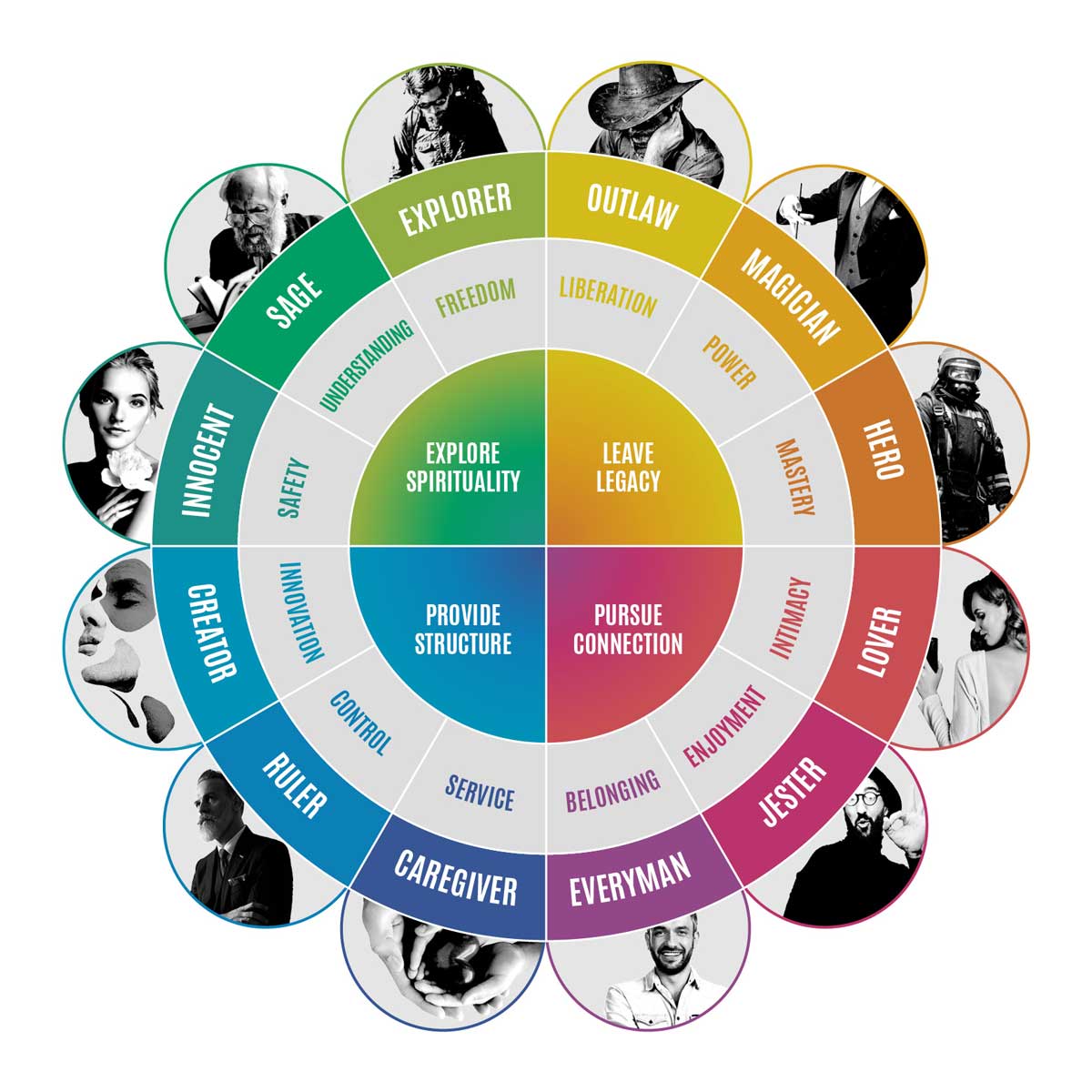
Archetypes in branding: The world's most loved brand all have personalities that we have a human connection with and they are developed on the framework called Brand Archetypes.
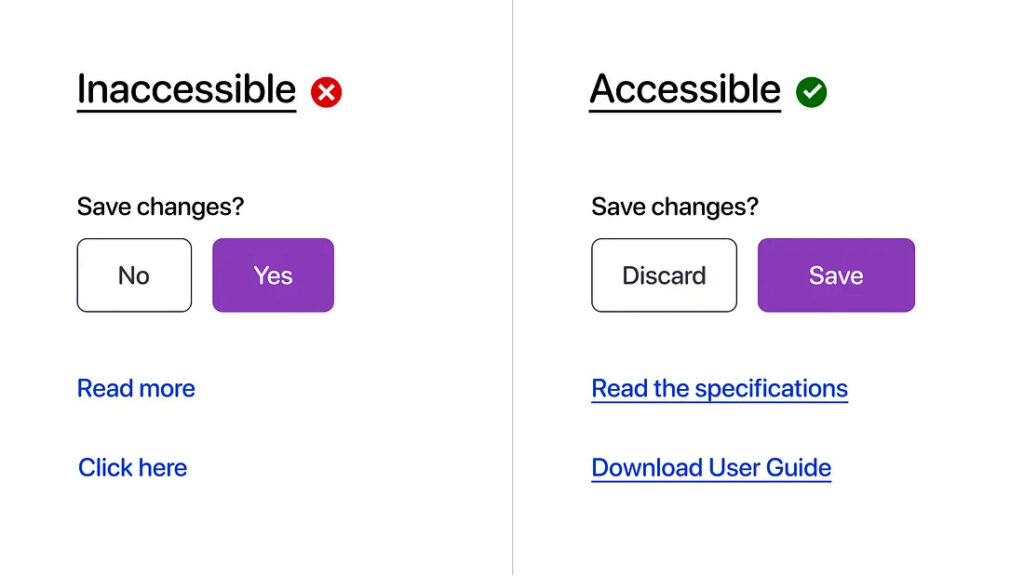
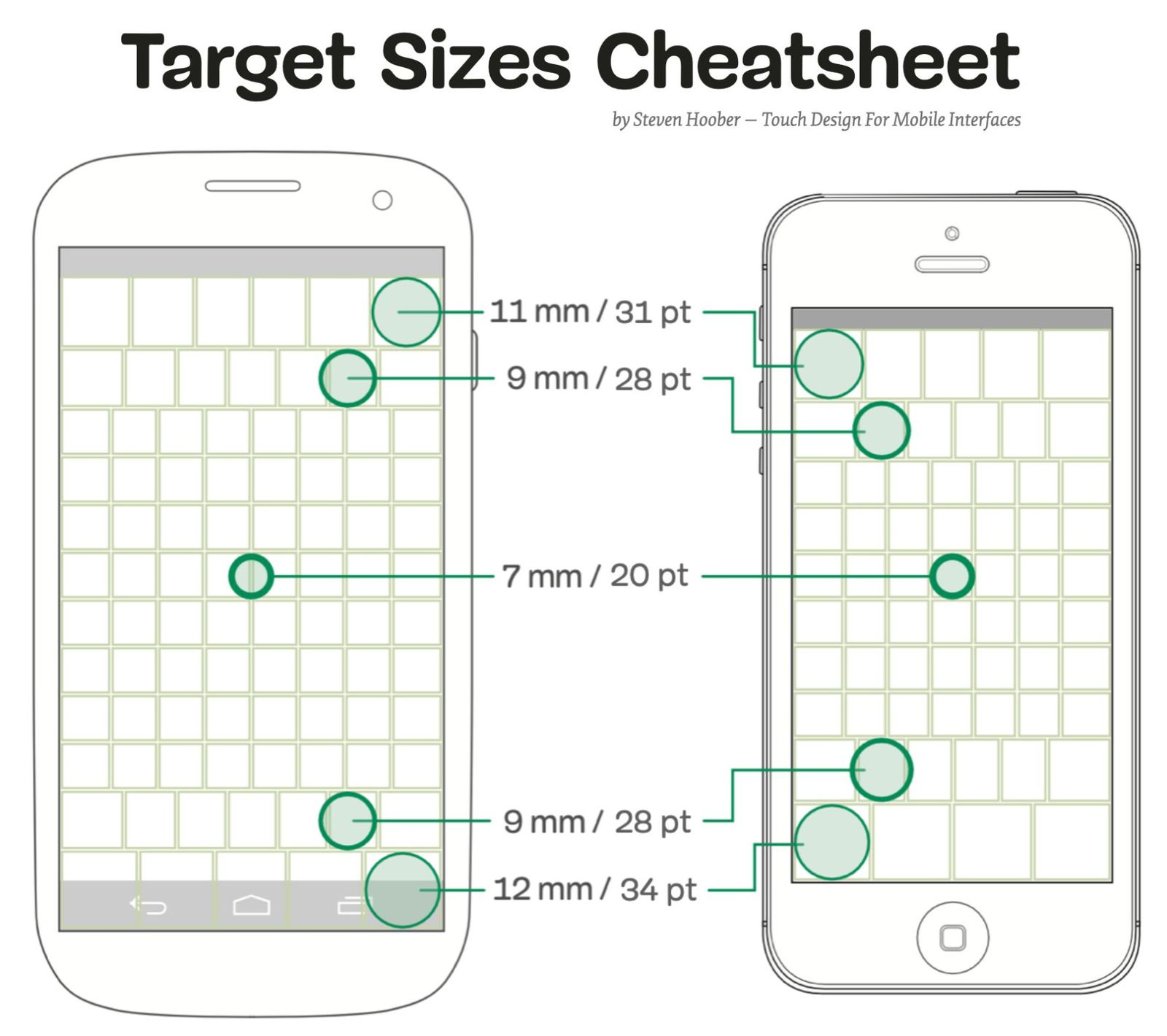
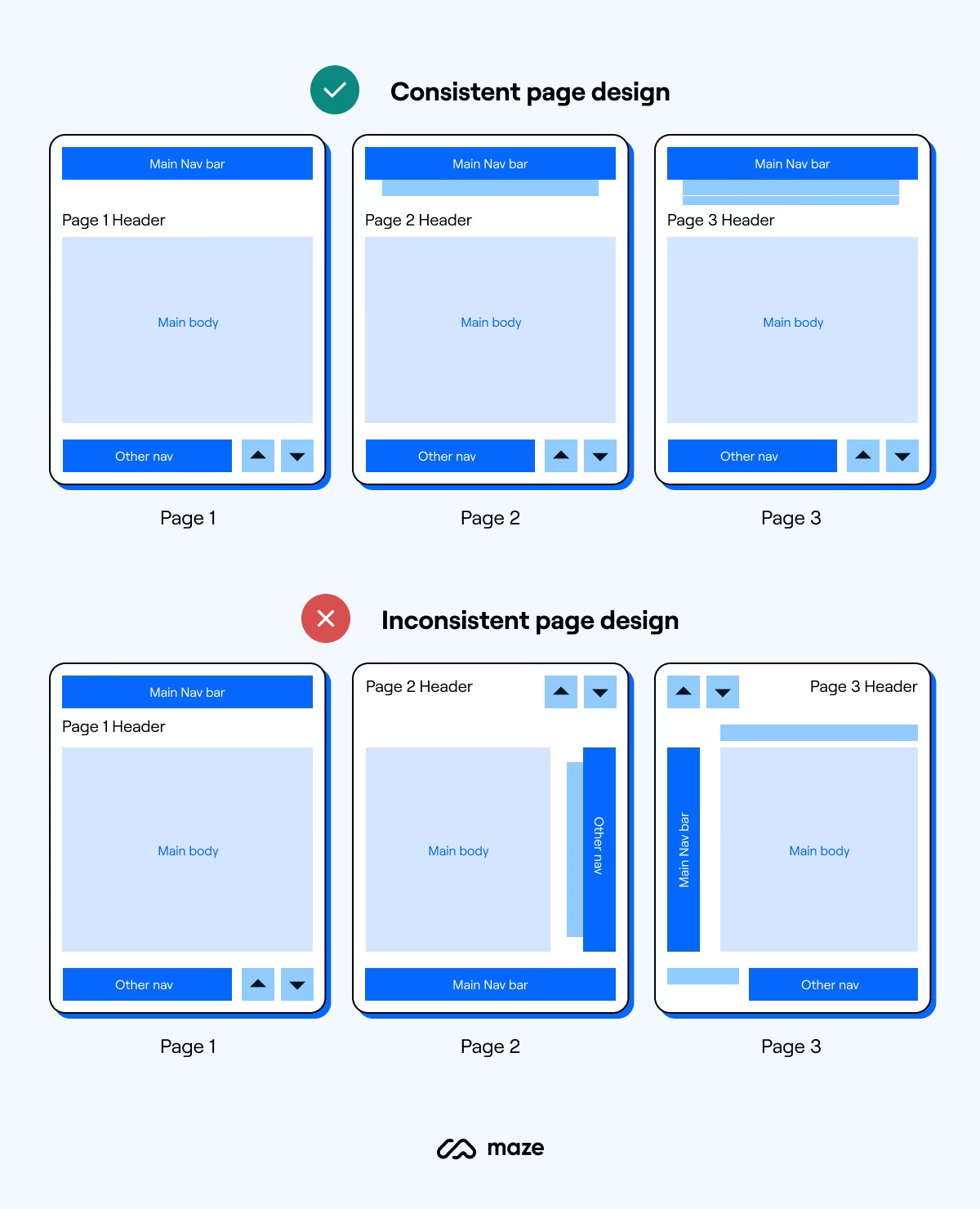
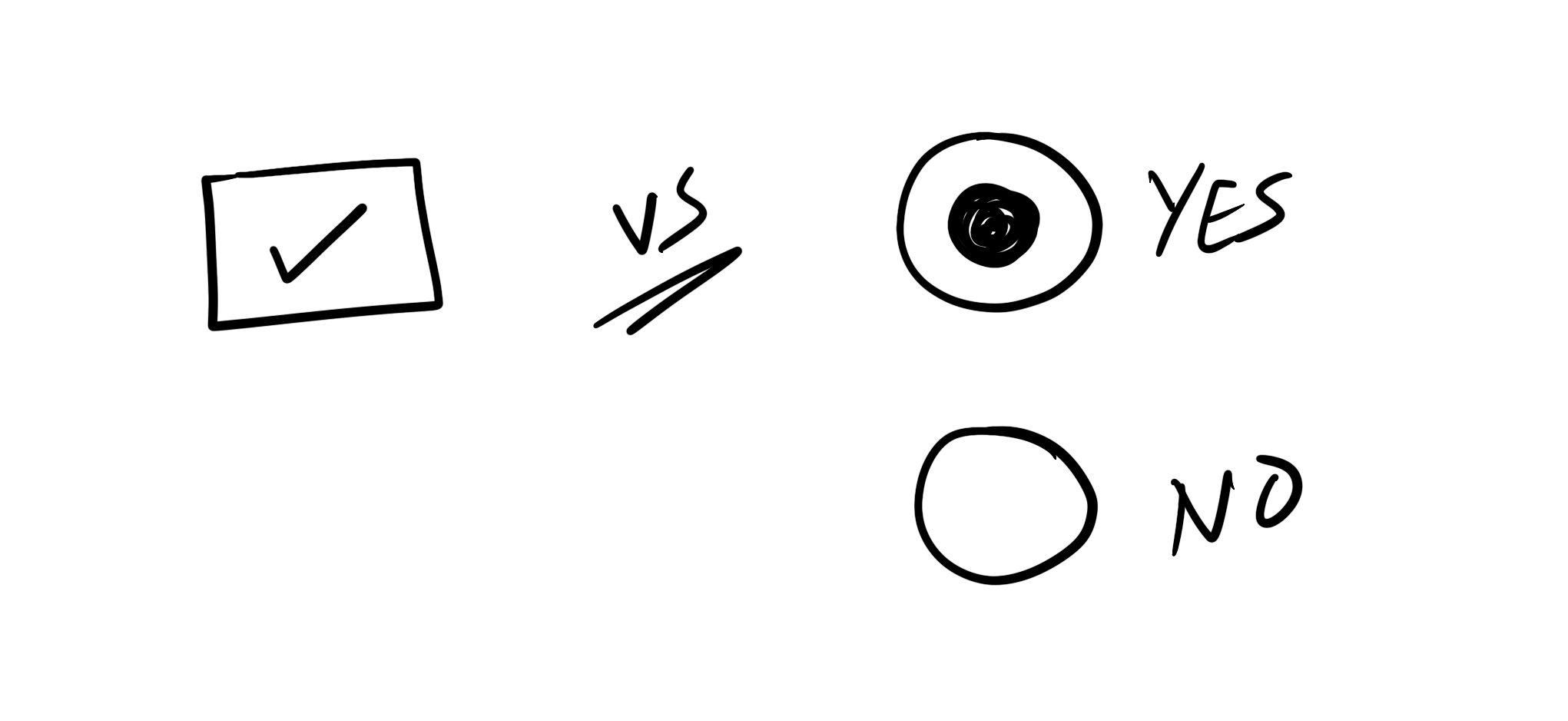
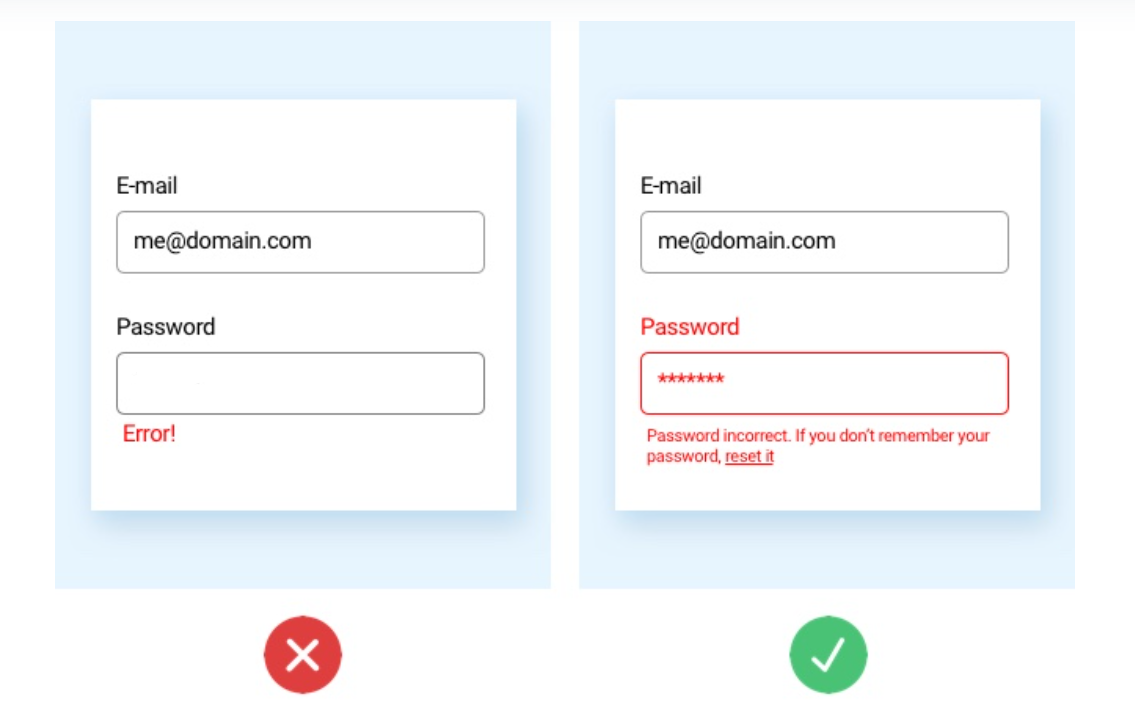
Understanding UI anti-patterns is crucial for effective web design. This guide highlights common pitfalls to avoid.